Enterprise Architecture (EA) planning and organization is the process of defining the use of information in support of the business and resourcing the practice for implementation and delivery. In a top-down approach, EA approaches the business process and operational needs, and develops the IT or applications plan to better align the business with IT through functional planning.
Planning and organizing EA is critical to a company’s performance by:
- Defining a strategic target state that aligns technology to the overall business objective
- Creating a roadmap that identifies the gaps
- Recommending a sequencing plan to bridge the gaps over a long-term time horizon and cost structure
Major Areas of influence of Enterprise Architecture
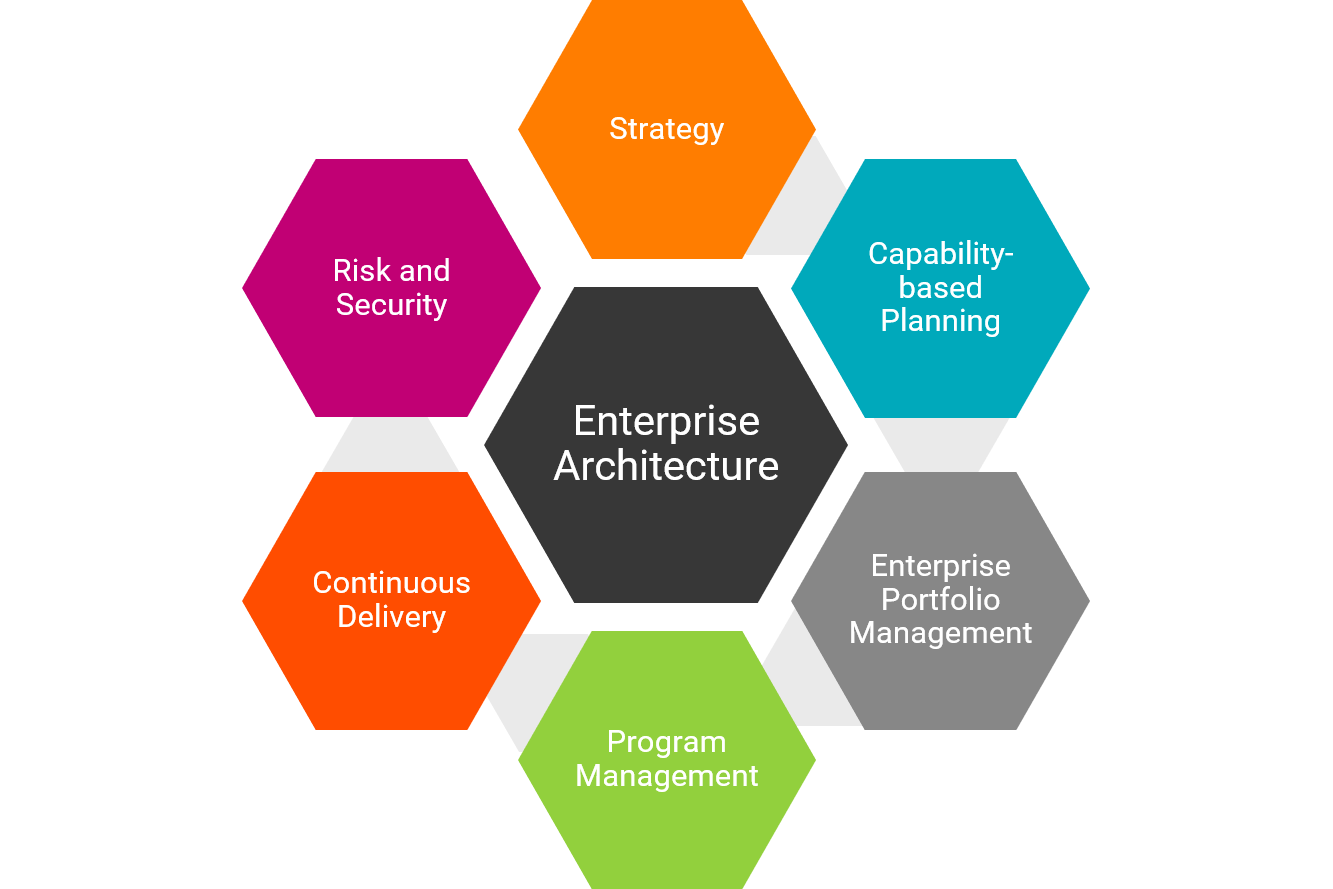
EA enables business delivery and architecture and encompasses oversight of major operational, organizational, technology, applications, data, and information decisions. While an IT discipline, EA is the glue that ties the business goals to the technical capabilities necessary to realize business objectives.
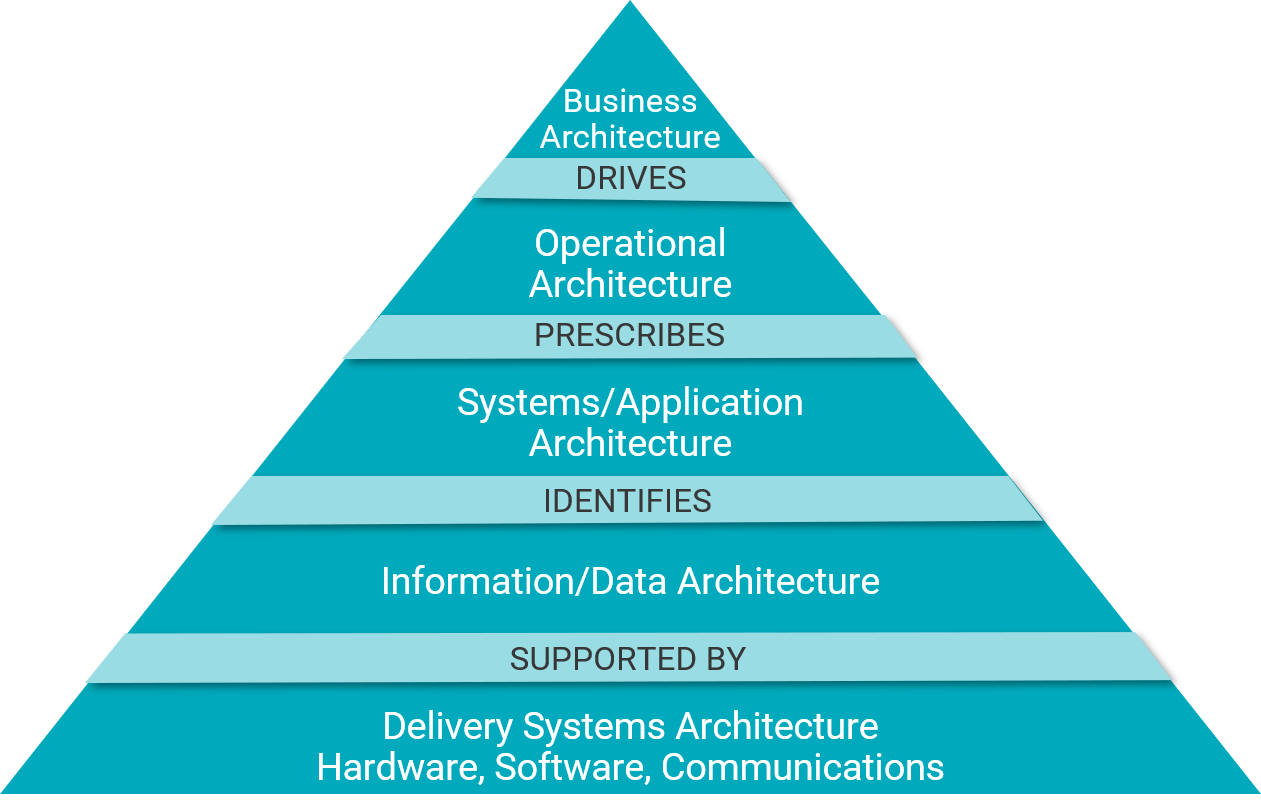
Business Architecture |
|
BA supports transformation program planning and business strategy development by providing target business architectures and an associated roadmap of new and enhanced business capabilities to enable the execution of those business strategies. This includes creating various business reference models, using these reference models for baseline assessment, conducting opportunity assessments for improving business performance, and creating integrated target architecture models to show future market positioning, product offering capabilities, enterprise structures, proposed business partner relationships, resource requirements, and placing these capabilities on a migration strategy to align with desired delivery timelines. These target models are used by business planning functions to structure, organize, and govern related business transformation programs. |
|
Operational Architecture |
|
OA supports program planning and operational strategy development by providing target operational architectures and an associated roadmap of new and enhanced operational capabilities to enable new business models and improve operational effectiveness. This includes creating service function and information reference models; using these reference models for baseline assessment; conducting opportunity assessments for improving operations; creating integrated target architecture models to show future operational process requirements, organizational structures with accountabilities, and resource requirements; and placing these capabilities on a migration strategy to align with related business and systems programs. These target models are used by operational planning and delivery functions to structure, organize, and govern related operational transformation programs. |
|
Application Architecture
|
Information / Data ArchitectureIA is responsible for creating the overall strategy for managing information with a view to contributing to the achievement of business goals and objectives through enabling operational efficiencies with effective information management solutions. It provides strategic guidance to operational, systems and technology planning to address information management opportunities. It also creates and maintains policies related to information management, security, and privacy in accordance with current and planned operational, system and technology requirements that underpin data products, facilitating discoverability and accessibility and minimizing data redundancy and fragmentation.
|
Technology ArchitectureTA describes the IT infrastructure required to support the development, deployment and support of applications, IT services, hardware, middleware, networks, platforms, etc. |
|
Enterprise Architecture |
|
High Level Enterprise Architecture Framework
Architecture Review Board
Purpose
The Architecture Review Board (ARB) serves as a governance body ensuring IT initiatives align with Ecosystem Architecture and ultimately align with business goals, strategies, and objectives. The ARB’s purpose is to improve the quality of an organization’s operations.
- The Architecture Review Board (ARB) defines appropriate IT strategies to support Business and Operational needs and ensures development alignment with those strategies.
- The ARB is responsible for defining technical design standards, policies, and principles for IT overall.
- The ARB is also responsible for all technical aspects of the IT portfolio such as providing guidance and approving project architecture (conducting technical feasibility studies), providing technical recommendations on architecture, and on design (e.g., best practice reviews).
Goals
The goals of the Architecture Review Board (ARB) include the following:
- Improve the quality of products and services the business offers
- Plan, design, and implement an efficient, effective, and comprehensive architecture for Infrastructure and Applications
- Establish an architecture baseline and develop and maintain a target architecture
- Establish and promote architecture best practices
- Create architecture roadmaps that align with business and operational roadmaps
- Lead the architecture review process
- Identify new technologies and retire redundant and outdated technologies
- Support an “Agile Mindset”
Roles and Responsibilities
The key roles and responsibilities of the Architecture Review Board (ARB) include the following:
Domain |
Role/Responsibility |
|---|---|
Decision Making |
|
| Escalation |
|
| Communication |
|
Ongoing Activities |
|
Ad-Hoc Activities |
|
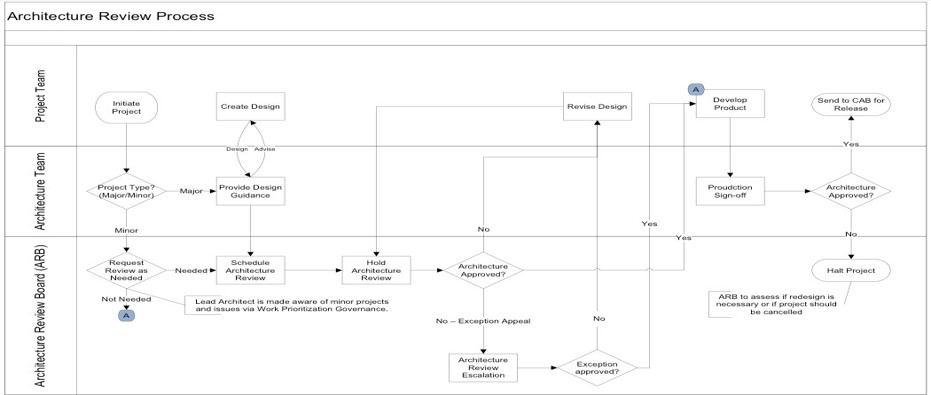
Architecture Review Process (End-to-End)
Sample Membership
The composition of the ARB primarily includes technical resources from IT who reside in the Ecosystem Architecture team as well as Business and Operational representatives from the Line of Business (LoB) Units. However, ARB will leverage subject matter experts as needed.
The membership of the ARB consists of the individuals identified below.
| Function | Name |
Team |
Role/Level |
|---|---|---|---|
| Chair | Platform & Systems Integration |
Director / Lead Architect |
|
Co-Chairs |
Enabling Team |
VP IT, VPs LoB |
|
| Member | Business/Operational SME |
LoB | |
| Member | Platform Engagement |
Community representative and Data Impacts |
|
| Member | IT Ecosystem Architecture |
Information Systems and Middleware |
|
| Member | IT Ecosystem Architecture |
Web Application Architecture |
|
| Member | Project & Portfolio Management |
Admin Systems |
|
| Member | IT Ecosystem Architecture |
Learning Management Systems |
|
| Member | Corporate Information Group |
Business Delivery |
Sample Meeting Frequency and Agenda
The ARB shall meet every two weeks. During critical time periods, the meeting frequency may be increased to meet program needs. Communications, guidance, and information such as meeting schedules, agendas, and minutes will be made available by the Chair or the Chair’s appointee.
The following high-level agenda outlines a potential framework for the structure of the meeting. Note that each agenda item may not necessarily be a topic at every meeting.
- Define IT Architecture best practices
- Evaluate potential and in-progress solution design(s)
- Update architectural and design standards
- Review action items
- Open discussion
Charter
Accountabilities
|
Composition
|
Inputs
|
Outputs
|
Mandate
|
Escalation Point for:
|
Frequency Every 2 weeks / Quarterly (Architecture & Innovation) |
|

